How To Use Div In Html
HTML <div> Tag
The <div> tag is an empty container that is used to ascertain a division or a section. It does not affect the content or layout and is used to grouping HTML elements to be styled with CSS or manipulated with scripts.
We recommend to use <div> tag simply when no other semantic elements introduced in HTML5 (such as <nav> , <master> or <article>) are advisable.
Since <div> is a block-level chemical element, a line break is placed earlier and subsequently it.
It is possible to place whatsoever HTML element within a <div> tag, including another <div>.
The <div> tag tin Non be inside <p> tag, because the paragraph will be broken at the point, where the <div> tag is entered.
To apply styles inside a paragraph use <span> tag, which is used with inline elements.
Syntax
The <div> tag comes in pairs. The content is written between the opening (<div>) and closing (</div>) tags.
Example of the HTML <div> tag:
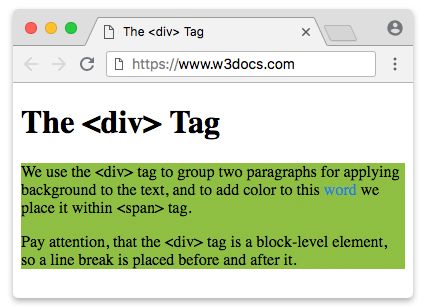
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>The <div> Tag</title> </head> <body> <h1> The <div> Tag </h1> <div style="background-color:#8ebf42"> <p>We employ the <div> tag to group two paragraphs for applying a groundwork to the text, and to add color to this <span style="color:#1c87c9">word</span> nosotros identify information technology within <bridge> tag.</p> <p> Pay attention, that the <div> tag is a block-level element, and so a line break is placed earlier and after information technology.</p> </div> </body> </html> When we build layouts, we bargain with multiple blocks defined by the <div> tag. The positioning of these blocks is at the eye of layout: placing elements in the correct relative positions across all screen sizes is 1 of the most important tasks.
Depending on the content and the goals of the page, we can use different techniques (or their combinations) to decide the place of each block. Let'south learn more about these techniques.
Flexbox ¶
In mod websites float-based layouts are existence replaced with Flexbox. The chief idea behind Flexbox is that with it, you can control the alignment, direction, social club, and size of the items inside the container.
Example of a Flexbox with HTML <div> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <caput> <title>Title of the document</title> <fashion> .flex-container { display: flex; align-items: center; /* Utilise another value to see the effect */ width: 100%; height: 200px; groundwork-color: #1faadb; } .flex-container > div { width: 25%; height: 60px; margin: 5px; border-radius: 3px; groundwork-color: #8ebf42; } </style> </caput> <body> <div grade="flex-container"> <div> </div> <div> </div> <div> </div> </div> </body> </html> CSS Bladder property ¶
CSS bladder property, or "floats" allows elements to announced adjacent to, or autonomously from, one another, which lets us create different types of layouts, including multi-column pages, sidebars, grids, etc.
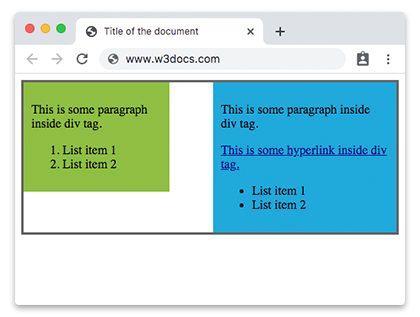
Example of the HTML <div> tag with the CSS float holding:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <caput> <championship>Championship of the certificate</championship> <style> .content { overflow: auto; border: 3px solid #666; } .content div { padding: 10px; } .content a { color: darkblue; } .blue { bladder: right; width: 45%; groundwork-color: #1faadb; } .dark-green { float: left; width: 35%; groundwork-color: #8ebf42; } </style> </caput> <body> <div class="content"> <div class="blue"> <p>This is some paragraph within div tag.</p> <a href="#">This is some hyperlink inside div tag.</a> <ul> <li>List item i</li> <li>List item 2</li> </ul> </div> <div class="light-green"> <p>This is some paragraph inside div tag.</p> <ol> <li>List item i</li> <li>List item 2</li> </ol> </div> </div> </body> </html> Result
Negative Margins ¶
Negative margins can exist applied to both static or floated elements.
Instance of negative margins:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Title of the document</championship> <style> .content div { padding: ii%; } .content a { color: darkblue; } .chief-content { width: thirty%; margin-left: 32%; } .bluish { width: 25%; margin-summit: -10%; background-color: #1faadb; } .greenish { width: 20%; margin: -35% auto auto seventy%; groundwork-color: #8ebf42; } </style> </head> <trunk> <div grade="content"> <div class="main-content"> <a href="#">This is some hyperlink inside div tag.</a> </div> <div class="blue"> <p>This is some paragraph inside div tag.</p> <a href="#">This is some hyperlink inside div tag.</a> <ul> <li>List item ane</li> <li>List item 2</li> </ul> </div> <div course="dark-green"> <p>This is some paragraph inside div tag.</p> <ol> <li>Listing particular 1</li> <li>List item 2</li> </ol> </div> </div> </body> </html> Relative+absolute positioning ¶
If you lot want to position div relative to item element you lot can employ a combination of position: relative and position: accented.
Case of relative+accented positioning of HTML <div> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Title of the certificate</title> <way> .content { position: relative; pinnacle: 400px; border: 1px solid #666; } .content div { position: accented; width: 35%; padding: 10px; } .blueish { correct: 20px; bottom: 0; background-color: #1faadb; } .green { summit: 10px; left: 15px; background-color: #8ebf42; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="content"> <div course="blue"> <p>This is some paragraph inside div tag.</p> </div> <div grade="green"> <p>This is some paragraph inside div tag.</p> </div> </div> </body> </html> position: relative does not bear on the positioning of elements in normal flow unless y'all add offsets.
Attributes ¶
The <div> tag also supports the Global attributes and the Event Attributes.
How to style <div> tag?
Common properties to modify the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in <div> tag:
- CSS font-mode belongings sets the style of the font. normal | italic | oblique | initial | inherit.
- CSS font-family unit property specifies a prioritized listing of one or more font family names and/or generic family names for the selected element.
- CSS font-size property sets the size of the font.
- CSS font-weight property defines whether the font should exist assuming or thick.
- CSS text-transform property controls text case and capitalization.
- CSS text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text, and is a shorthand property for text-decoration-line, text-decoration-color, text-ornament-fashion.
Coloring text in <div> tag:
- CSS colour property describes the colour of the text content and text decorations.
- CSS background-color property sets the background colour of an element.
Text layout styles for <div> tag:
- CSS text-indent belongings specifies the indentation of the first line in a text block.
- CSS text-overflow property specifies how overflowed content that is non displayed should be signalled to the user.
- CSS white-infinite property specifies how white-space inside an chemical element is handled.
- CSS word-break property specifies where the lines should be broken.
Other properties worth looking at for <div> tag:
- CSS text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
- CSS text-marshal-last property sets the alignment of the last line of the text.
- CSS line-summit holding specifies the height of a line.
- CSS letter-spacing property defines the spaces between messages/characters in a text.
- CSS give-and-take-spacing belongings sets the spacing between words.
How To Use Div In Html,
Source: https://www.w3docs.com/learn-html/html-div-tag.html
Posted by: sancheznernat.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Use Div In Html"
Post a Comment